Our Science
Our therapeutics are founded on the novel scientific discovery of a pathway, the IGFBP3/TMEM219 axis, found to be involved in stem cell apoptosis in the gut, as well as pancreatic and other tissues.
IGFBP3/TMEM219 pathway
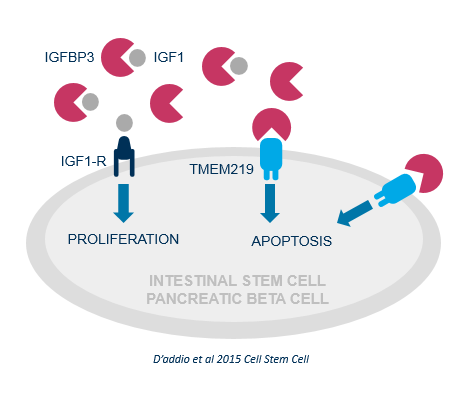
The IGFBP3/TMEM219 (Transmembrane Protein 219) axis is a novel apoptosis pathway involved in stem cell apoptosis in the gut, pancreas and other organs.
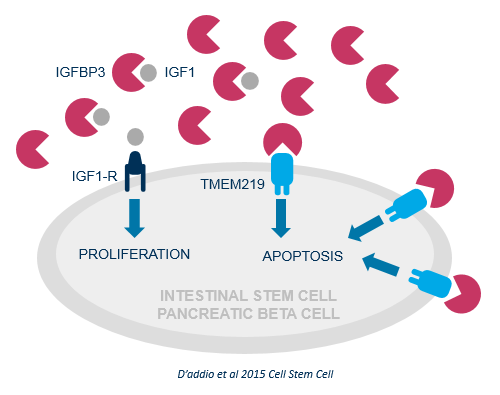
Imbalances in the IGFBP3/TMEM219 pathway as a result of excess IGFBP3 trigger differentiated and stem/progenitor cell apoptosis in the gut crypts and pancreas, playing a key role in the development and progression of intractable diseases such as autoimmune Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) and Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).
A novel pathway: IGFBP3/TMEM219 axis
IGFBP3/TMEM219 axis dysregulation in T1D and IBD patients
Pathway dysregulation associated with intractable disease onset and progression
The IGFBP3/TMEM219 pathway is controlled by a tightly regulated, dynamic balance between the TMEM219 receptor and its ligand, IGFBP3.
Research at the San Raffaele Hospital, Milan, Italy highlighted that imbalances in the pathway, as a result of abnormally high levels of IGFBP3, lead to mass cell death.
High levels of IGFBP3 have been found in T1D and IBD patients. As the pathway controls beta cells and the colonic stem cell mass, its dysregulation leads to stem cell apoptosis in the gut, pancreas and other tissues.
Novel therapeutic concept
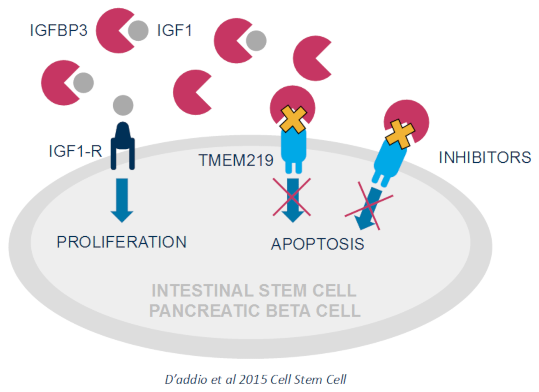
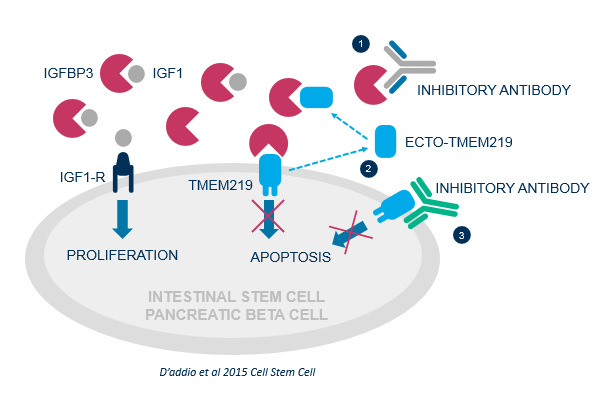
Our unique therapeutic approach consists of targeting the IGFBP3/TMEM219 axis and its dysregulation to re-establish organ function in patients suffering from autoimmune disorders where elevated levels of IGFBP3 have been found.
Our pipeline is derived from a proven discovery engine that identifies biologic therapeutic candidates that are capable of inhibiting the axis using multiple approaches at different stages of the pathway.
The selective inhibition of IGFBP3 represents a new modality, opening up numerous opportunities to abrogate cell apoptosis and revert the outcome of several underserved autoimmune diseases.
Targeting the IGFBP3/TMEM219 axis to re-establish organ function in T1D and IBD patients